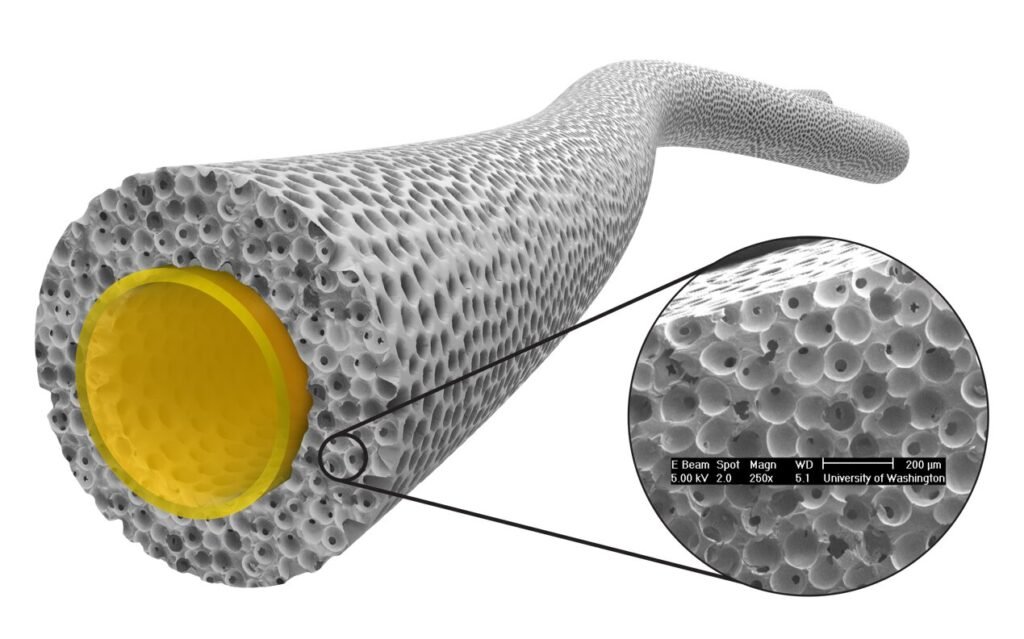
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are a leading cause of mortality worldwide, responsible for nearly 18 million deaths annually. As populations age and sedentary lifestyles increase, the global burden of CVDs is rising. In this context, vascular grafts have emerged as a cornerstone in addressing life-threatening cardiovascular conditions. These medical devices are used to bypass blocked blood vessels, repair aneurysms, or provide access for dialysis. As healthcare systems evolve, vascular grafts are becoming increasingly vital in cardiovascular care, offering hope to millions of patients.
The Role of Vascular Grafts in Modern Medicine
Vascular grafts play a critical role in various medical procedures. One of their primary applications is coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG), where they are used to reroute blood around clogged arteries, restoring adequate blood flow to the heart. This procedure is a lifesaving intervention for patients with severe coronary artery disease.
In addition to CABG, vascular grafts are instrumental in creating durable access points for patients undergoing hemodialysis. Individuals with kidney failure rely on these grafts for effective blood filtration, improving their quality of life. Moreover, aneurysm repair is another significant application of vascular grafts. Endovascular grafts, designed specifically for minimally invasive procedures, help repair bulging or weakened blood vessels, particularly in the abdominal aorta, preventing life-threatening ruptures.
Types of Vascular Grafts
Vascular grafts come in various forms, each suited for specific medical needs:
- Synthetic Grafts: Manufactured from materials like ePTFE (expanded polytetrafluoroethylene) and polyester, synthetic grafts are known for their durability and resistance to infection.
- Biological Grafts: Derived from animal tissues, these grafts provide better biocompatibility, reducing the likelihood of rejection and improving integration with natural tissues.
- Composite Grafts: Combining synthetic and biological materials, composite grafts offer enhanced functionality, catering to complex medical cases.
Market Dynamics Driving Growth
The global vascular grafts market is expanding rapidly, fueled by several factors. The rising prevalence of CVDs is a major driver, with increasing cases of heart diseases propelling demand for advanced treatment options. Additionally, technological advancements in graft materials and designs are enhancing patient outcomes and reducing post-surgical complications.
The growing geriatric population is another critical factor. Older adults are more susceptible to vascular diseases, creating a significant need for vascular grafts. Furthermore, the market is witnessing geographical expansion, with developing regions investing in healthcare infrastructure to address cardiovascular health issues.
Challenges in Adoption
Despite their importance, vascular grafts face challenges that hinder widespread adoption. One of the primary obstacles is high costs. Advanced grafts and associated surgical procedures remain expensive, limiting accessibility for patients in low-income regions. Additionally, post-surgical complications such as infection, thrombosis, and graft rejection present challenges for patients and healthcare providers. The lack of skilled professionals in developing regions further exacerbates these issues.
Future Trends in Vascular Grafts
The future of vascular grafts is bright, with promising innovations on the horizon. 3D printing technology is paving the way for personalized vascular grafts tailored to individual patient anatomy, minimizing rejection risks and improving surgical outcomes.
Nanotechnology is another game-changer, enabling the development of grafts with antimicrobial properties and enhanced biocompatibility. Additionally, advances in tissue engineering are leading to the creation of fully biocompatible grafts derived from patient cells, significantly reducing the risk of complications.
Conclusion
Vascular grafts are revolutionizing modern cardiovascular care, saving lives and improving outcomes for millions of patients. While challenges like cost and accessibility persist, continued innovations in technology and material science are addressing these barriers. By fostering equitable access to these lifesaving devices, the healthcare industry can ensure that vascular grafts reach those in need, transforming the landscape of cardiovascular treatment.